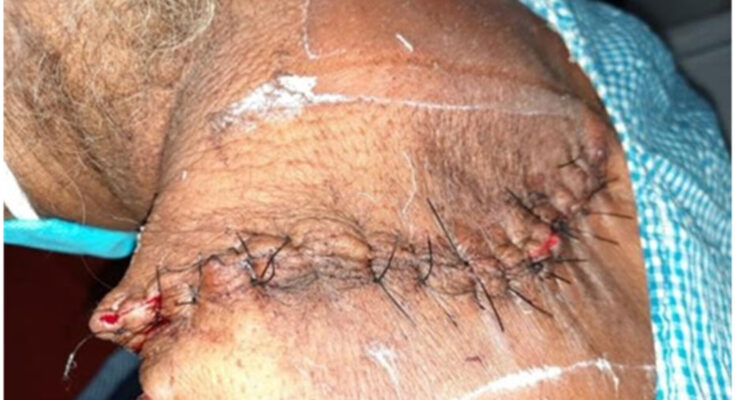
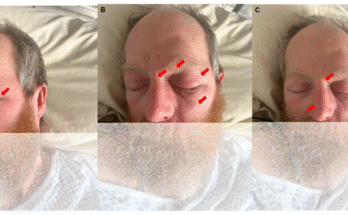
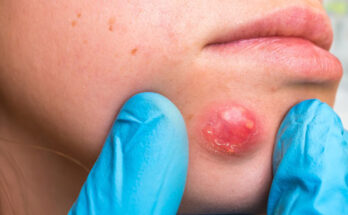
An infected sebaceous cyst is a painful lump that forms under the skin when an oil gland becomes blocked and bacteria enter the area. At first, a sebaceous cyst is usually harmless and appears as a small, smooth bump. However, if it becomes infected, the cyst can grow larger, turn red, swell, and fill with pus. This can cause discomfort, tenderness, and sometimes a foul-smelling discharge if the cyst bursts.
The main causes of infected cysts include blocked oil glands, bacterial infection, or irritation of the skin. People with oily skin, acne, or repeated skin injuries may be more likely to develop them.
Common symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, warmth in the affected area, and pus drainage. In some cases, the infection can spread to nearby tissues, making the condition more serious if not treated in time.
Treatment usually depends on the severity of the infection. Doctors may drain the pus, prescribe antibiotics, or surgically remove the cyst to prevent it from coming back. It is important not to squeeze or pop the cyst at home, as this can make the infection worse.
Good skin care, keeping the area clean, and avoiding unnecessary pressure on the skin can help reduce the chances of developing infected sebaceous cysts. If a lump becomes painful or shows signs of infection, medical help should be sought as early as possible.